
The most common AV ratio is 2:1, resulting in a ventricular rate of ~150 bpm
Ventricular rate is determined by the AV conduction ratio (“degree of AV block”). The length of the re-entry circuit corresponds to the size of the right atrium, resulting in a fairly predictable atrial rate of around 300 bpm (range 200-400) It has been updated.ĭownload a copy of the guide: 10 tips to identify atrial flutter.Atrial flutter is a form of supraventricular tachycardia caused by a re-entry circuit within the right atrium. Read next: Training Day: Mastering the 12-lead With these tips and practice, you will be much less likely to mistake atrial flutter with 2:1 conduction for another tachycardia. You will learn to see the rhythm strip as separate atrial activity and ventricular activity portions and the hidden flutter waves will stand out for you. Look at as many strips of confirmed 2:1 conduction as you can and your eye will become trained to see it. Now that you are more aware of atrial flutter with 2:1 conduction, the best way to get good at recognizing it is regular practice. You might consider using a Lewis lead, which enhances detection of atrial activity. In some leads, atrial flutter will not have a sawtooth pattern. A 12-lead ECG can help immensely in seeing the flutter waves, because some leads are better for viewing atrial activity than others. Use more than one leadįor rhythm interpretation, the more leads the better. By evaluating the P waves, QRS complexes, intervals and rate, you may discover that your first impression was wrong. Get your first impression, then think of alternate diagnoses and apply rhythm interpretation criteria. Most people with sinus tach, especially over 130 bpm, will usually have a readily-apparent reason for the tachycardia, like fever, fear, pain, anxiety, exertion, drugs, hypovolemia or hypoxia. You see no obvious reason for sinus tachycardiaĬonsider atrial flutter if the patient has no obvious reason for sinus tachycardia. Re-entrant tachycardias hit a fast rate suddenly and maintain that rate until they end suddenly. For example, if your patient talks or moves around in bed, the rate may go up slightly. Remember that sinus rhythms tend to fluctuate slightly. 
Suspect any tachycardiaĪny rhythm around 150 bpm should be suspected of being atrial flutter with 2:1 conduction. Here are 10 tips to avoid missing atrial flutter. You won't find atrial flutter it if you aren’t looking for it. 10 tips to avoid missing atrial flutter with 2:1 conduction. As cardiac output is decreased and cardiac workload increased, ventricular fibrillation can result. In patients with accessory pathways that bypass the slow conduction of the AV node, like Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome, 1:1 conduction of atrial flutter or atrial fib can be life-threatening. Atrial flutter can lead to fast rates at 2:1 conduction, and VERY fast rates at 1:1 conduction. When we see slower ventricular rates and conduction ratios of 3:1 or more, it is usually due to medications or other causes of enhanced refractoriness of the AV node. New-onset atrial flutter is most often conducted 2:1, because that is a comfortable rate (around 150 per minute) for the AV node to conduct. The AV node is bombarded by a regular atrial rhythm of around 300 per minute.
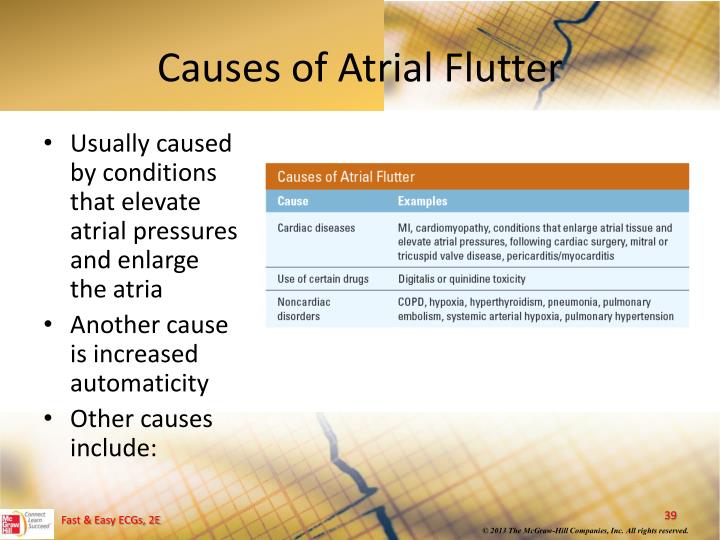
It can occur suddenly, and is sometimes associated with periods of atrial fibrillation. Atrial flutter is a re-entrant tachycardia that occurs in the atria.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
